Key facts about Blockchain
- Blockchain is a type of database
- It is a common register of transaction
- It is a peer to peer network
- It is Decentralized (It doesn’t have one central entity taking control of the system)
- But the most important property of a Blockchain is that it is immutable (Once some data is recorded inside of it, it is irreversible)
- Blockchains are most commonly used as ledgers for transactions which are sometimes referred to as Data Ledger Technology (DLT)
Blockchain Defined
Simply it is defined as a type of database which is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records the provenance of a digital asset. By inherent design, the data on a Blockchain is unable to be modified, which makes it a legitimate disruptor for industries.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain as the name suggests is a chain of blocks that contains information. Blockchain may seem complicated but its core concept is quite simple. A Blockchain is a database that stores encrypted blocks of data then chains them together to form a chronological single-source of truth for the data. These data contain digital assets which are distributed instead of copied or transferred which creates an immutable record of an asset. These assets are decentralized which allows real-time access and transparency. Having transparency on ledgers preserves the integrity of the documents that create trust in the asset. Blockchains’ security measures and public ledgers make it a prime technology for every single sector.

How does Blockchain work?
“The whole point of using a blockchain is to let people — in particular, people who don’t trust one another — share valuable data in a secure, tamperproof way.”
MIT Technology Review
There are 3 main components,
1) Blocks
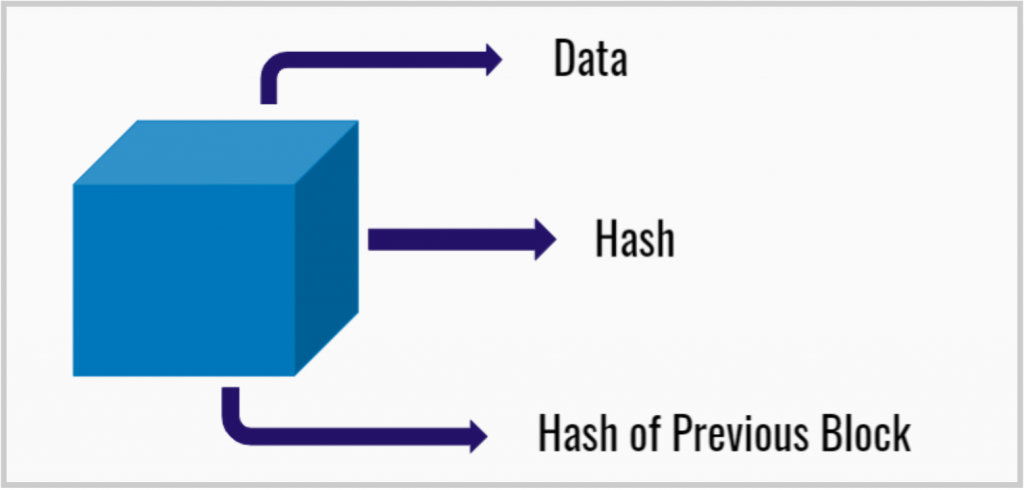
Every chain consists of blocks which consist of 3 sub-elements
- Data – The basic data stored in the block
- Nonce – The nonce is a randomly generated number when a block is created which in return generates the block header hash.
- Hash – It’s a 256-bit number wedded to the nonce. In a Blockchain when the first block is created, a nonce generates the cryptographic hash. The block is considered signed and forever tied to the nonce and hash unless it is mined which will be explained below.
2) Miners
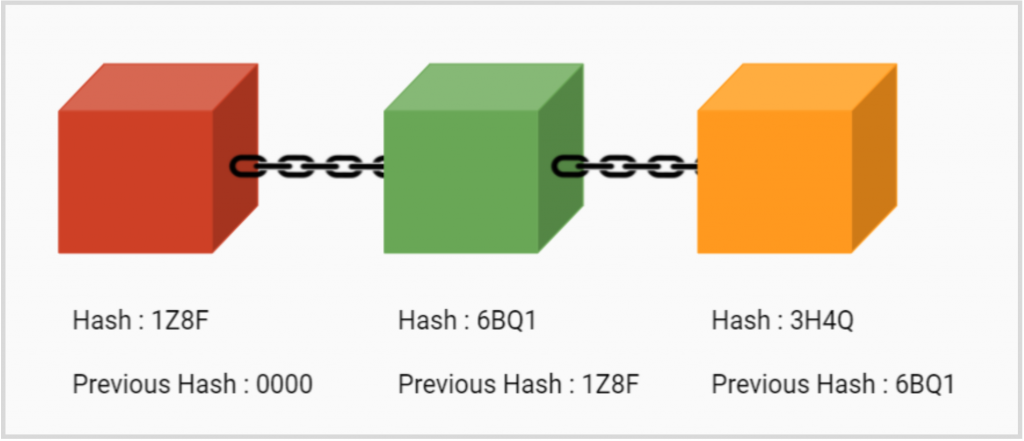
Miners create new blocks on the chain through the mining process. Mining blocks is not easy as each block not only contains the nonce and hash of its block but it contains the nonce and hash of the block created before it as well.
Making changes to any block earlier in the chain requires re-mining. when a single block is changed all the blocks that come afterward also need to be changed in the process. As a result, it becomes extremely difficult to manipulate Blockchain technology. When a block is successfully mined, the change is accepted by all the nodes of the network and the miner is rewarded financially.
3) Nodes
One of the most important concepts in Blockchain technology is decentralization. Not one single organization or device can own a chain but instead, it is a distributed ledger via the connected nodes of the chain. Nodes can be any electronic device that keeps the network functioning. Every node has a copy of the Blockchain and should approve every newly mined block for the chain to be updated. Every transaction in the ledger can be viewed by each participant easily since Blockchains are transparent. Each of these participants is given a unique number to show their transactions.
This helps Blockchain maintain the integrity and creates trust among users. Essentially, Blockchain can be considered as a scalability of trust through technology.
Storage structure of a Blockchain
A Blockchain is considered to be a database as it stores information in data structures called blocks. However, while a Blockchain can be considered as a database, a database is not a Blockchain. They are not interchangeable as they differ in design. There is also a difference in the purpose between the two. In simple terms, a Blockchain collects information into a block. Each block has a certain storage capacity and when filled, they are chained. Forming a chain of data known as “Blockchain”.
All new information that follows the freshly added block is compiled into a newly formed block which will then also be added to the chain once filled.
Industrial sectors disrupted by a Blockchain
- Money Transfer
- Internet of Things (IOT)
- Personal Identity Security
- Health Care
- Supply Chain and Logistics
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- Cryptocurrency exchange
- Voting mechanism
Blockchain applications go far beyond cryptocurrency and bitcoin. With the ability to create more transparency, fairness, efficiency, and money-saving the technology impacts a variety of sectors. Below are a few companies that use Blockchain in real-world scenarios. It’s far from an exhaustive list, but they’re already changing how we do business.

Advantages and disadvantages of Blockchain?
Blockchain’s unique characteristics address many business issues. Blockchain can provide multiple advantages to businesses. It may be a public or private Blockchain network or permission-based Blockchain application. While there may be significant pros to the Blockchain. There are also a number of challenges and roadblocks.
These cons may not only be technical but political and regulatory as well.
Here are some selling points and challenges faced by businesses that are on market today.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High accuracy by low Human involvement | Technology cost |
| Cost reduction | Illegal Activity |
| Decentralization makes it hard to tamper with | Regulation |
| Transactions are secure, private, and efficient | Integration |
| Transparent technology | Scalability Issue |
| Immutability | Expertise Knowledge |
| Individual control of data | |
| Tokenization |
The future of Blockchain.
New innovations are constantly entering the new market with bolder uses of technology. Blockchain networks continue to bring real and transformative change to a number of industries. As stated, “ modern problems require modern solutions”. The future of the environment rests in the global adoption of Blockchain technology.
As we are headed to the third decade of Blockchain, it’s not a matter of “if” but “when” will the companies catch on to the technology is the question to be asked.
References
- Blockchain Explained, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp.
- Databases and Blockchains, The Difference Is In Their Purpose And Design, https://hackernoon.com/databases-and-blockchains-the-difference-is-in-their-purpose-and-design-56ba6335778b.
- Top 10 benefits of blockchain technology for business, https://searchcio.techtarget.com/feature/Top-10-benefits-of-blockchain-technology-for-business.
- Top Disadvantages Of Blockchain Technology, https://101blockchains.com/disadvantages-of-blockchain/.
- How does a Blockchain work – Simply Explained, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSo_EIwHSd4.